When Does Botox Kick In?
You've been waiting for days, but nothing's changed. Why does it take so long for Botox to kick in? We'll explain when it starts working and what to do for best results.
When does Botox kick in and when does it start working? These are two different questions:
- When does it start working: Means when does it start to effect the muscle.
- When does it kick in: Means when can you expect to see the full, final results.
We'll explain the difference and tell you what you should and should NOT do for the quickest and best results.
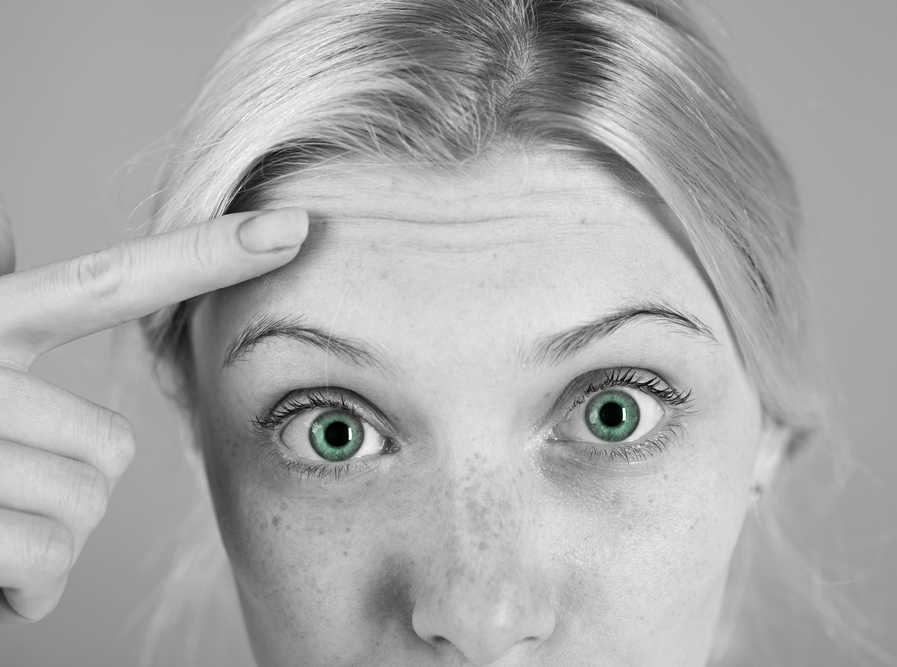 When will my Botox kick in?
When will my Botox kick in?When Does Botox Start Working and Kick In?
Botox starts working as soon as it's injected—but don’t expect instant results. Here's what you need to know:
The Timeline
- Day 1: Botox gets to work immediately by targeting nerve signals to the muscles.
- Days 3-5: You may start to notice subtle changes, like less muscle movement.
- Days 7-14: The full effects kick in, leaving you with smooth, relaxed skin.
Why Does It Take So Long?
Botox needs time to bind with certain muscle-moving proteins. As these proteins become less active, your muscles relax, and wrinkles soften. This process doesn't happen overnight—it’s gradual.
ABZ Quick Tip
Want faster results? Try muscle exercises, like forehead raises or scowls, to help speed things up. But don’t massage the area—this can cause the Botox to spread where it shouldn’t.
What happens after Botox is injected and why so long to see results?
Once Botox is injected, it starts working right away by blocking signals between the nerves and muscles. It attaches to proteins that control muscle movement and lowers the release of a chemical called acetylcholine, which helps muscles move.
But it takes a few days for enough acetylcholine to be blocked, so you won’t notice your muscles not moving right away. That’s why it takes a few days to see the full effect.
And in the case of a Botox lip flip, it might take even longer to see full results.
(Source: "In the presynaptic terminal, released light chains of BoNT enzymatically destroy one of the SNARE proteins. The SNARE proteins are being continuously made, so the time from injection to weakness depends on how long it takes to block enough proteins to stop muscle movement.") 1
How can I make Botox kick in faster?
How to speed up Botox results: Here are some tips on what you can do and should NOT do to help it kick in faster.
While there is nothing you can do to get immediate results, there are a few things to consider, for getting the best results quickly.
1. Supplements
Supplements: Some studies indicate that taking the supplement zinc a few days before and a few days after injections can help it last longer and possibly kick in faster.2
Click here for more info and dosage suggestions.
2. Muscle contractions
A study in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology suggests that muscle contractions can speed up the effects of Botox.
Research shows that moving or contracting the treated muscles helps speed up toxin uptake, potentially leading to quicker results.
The study focused on the forehead and glabella (the area between the eyebrows), with promising results. Some participants saw improvements days earlier than those who didn’t exercise their muscles!
For example, if you had injections for forehead (glabella) wrinkles:
- Try doing 3 sets of 40 scowls or 40 forehead raises,
- Do this three times a day.
- Take a 10-15 minute break between each set.
Researchers believe that exercising or moving the muscles helps Botox bind more quickly, which may bring results faster than usual.3
ABZ Tip: Avoid rubbing or massaging the injected area for 24-72 hours after treatment, as this could spread the toxin. Always check with your provider before trying any exercises.
3. Avoid cold compress?
The advice to avoid cold compresses after Botox injections is based on some studies, but it's not universally agreed upon.
Cooling the treated area might interfere with Botox uptake, as temperature can affect how the toxin binds to nerve endings. This could slow the effectiveness in some cases, but it’s not a proven fact, and different practitioners may have varying recommendations.4
For bruising, it's generally better to avoid cold compresses, as they can sometimes make bruising worse. Instead, try Arnica gel or taking Tylenol (acetaminophen), which can help with swelling and discomfort. Avoid blood thinners like aspirin before and after to reduce the risk of bruising, as these can increase bleeding.
Always follow your healthcare provider's advice based on your specific situation. If you're unsure, check with your injector or doctor for the best aftercare.
Why does Botox work faster in some areas
The areas that usually respond quicker are the smaller or weaker muscles, like those around the forehead or crow's feet area.
Areas with strong facial muscles may take a little longer for the treatment to take effect. Do not worry if you’re one of these people. You can enjoy the rejuvenating, wrinkle-eliminating effects of Botox, too.
For areas with particularly deep lines or those who are getting their first injection late in life, more than one injection may be necessary to see the desired results.
Final Takeaway:
Botox begins working immediately after injection, but the full effects can take anywhere from 7 to 14 days to appear. While you can't rush the process, simple actions like muscle contractions may help speed up results.
For the best outcome, follow your provider's aftercare advice and be patient as Botox gradually works its magic.
If you're not satisfied with your results and feel you need another injection, follow this guide on How Soon Can I Get Another Botox Injection.
And don't miss out on the top 10 Benefits of Botox and the 4 key Mistakes to Avoid to help prevent facial aging
When Does Botox Kick In: FAQ's
If you have any questions, please feel free to ask.
Q: Can you reverse Botox treatments?
Q: Can you reverse Botox treatments?
A: Unfortunately, no, you cannot reverse Botox injections. If you don't like the results, you'll have to wait a few months until it wears off.
Well, actually, Botox doesn't wear off, your muscle proteins (the ones responsible for muscle movement) take over.
Here is how it works:
When Botox is injected, it binds up SNARE proteins, which are necessary to make muscle movements.
However, the body is constantly making more of these proteins, so over time, as these proteins build up, you eventually gain control over your muscles. Read more about it here...
Q: What does it feel like when Botox kicks in?
Q: What does it feel like when Botox kicks in?
A: Depending on where your injection was, you might feel a slightly tight sensation or a feeling of heaviness. However, in general, most people can't feel Botox working. But, can see it when they try moving the injected muscle area.
Q: Can you see Botox results in 24 hours?
Q: Can you see Botox results in 24 hours?
A: No. While Botox starts working as soon as it's injected, most people will not start to see any results for about 3-5 days. And full results (when Botox kicks in) is usually seen in about 10-14 days.
Q: How does Botox work?
Q: How does Botox work?
A: Botox works to reduce the appearance of wrinkles. When Botox is injected into facial muscles, the muscles in the treatment area become immobilized.
When muscles can't move, the overlying skin (with static lines and deeper dynamic wrinkles) begins to relax and smooth out. By relaxing facial expressions, many people take on a more youthful appearance.
Q: How do I know if my Botox is working?
Q: How do I know if my Botox is working?
A: After about 3-5 days, you might feel a tight sensation around the injection area. Then, about a week after that, most people notice their dynamic lines (these are wrinkles that develop from constant and repetitive facial expressions) start to soften and become less visible.
If your wrinkles are still visible after 2 weeks, you might need more Botox and you should consult with your provider.
Q: Which Botox lasts the longest?
Q: Which Botox lasts the longest?
A: At this time, DAX (Daxxify) is the longest lasting neurotoxin. Instead of lasting 3-4 like the other neurotoxins, Dax can last up to 8 months.
DAX also is reported to kick in several days faster than other Botox brands.
DAX is made with a synthetic peptide that allows it to stay bound to the receptors at the neurosynaptic junction longer.
Receptors located at the neurosynaptic junction are responsible for muscle contraction. The longer they stay bound-up, the longer the results will last.
Want More?
I share quick routines, beauty tweaks, and what’s working for me — straight to your inbox. Join the Club and get this free Cheek Shaper Video.
About the Author:
Linda Robison is a Facial Fitness Specialist and the founder of Anti-Aging Beauty Zone. With decades of hands-on experience, she shares practical, natural ways to lift and brighten mature skin—without expensive or invasive treatments.
Before you go ....
Please tap on the💙in the bottom right corner if you found this page helpful.
FOLLOW ME FOR MORE TIPS:
SHARE OR SAVE FOR LATER: